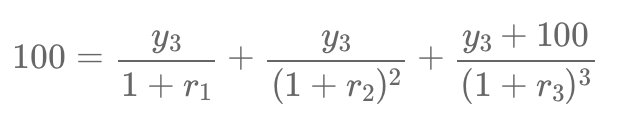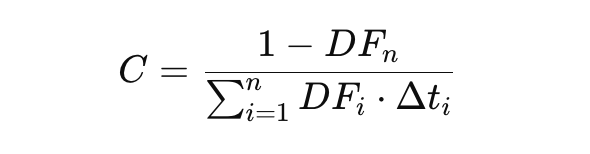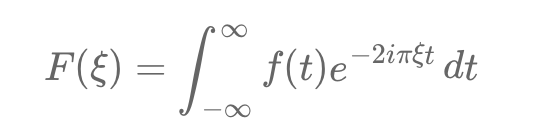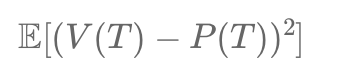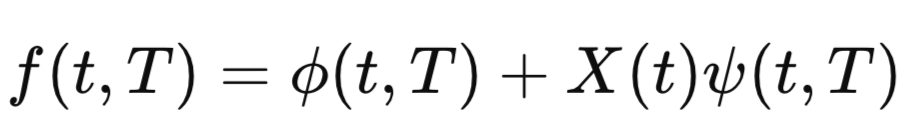Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 05. mars 2025
Learn how the Carr & Madan method leverages the Fourier Transform for option pricing. Discover key concepts, how to mitigate instabilities, and improve numerical computations.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 02. février 2025
In fixed-income markets, spot rates are crucial for pricing bonds and detecting arbitrage opportunities. However, financial markets typically provide par rates instead of spot rates, making it essential to extract missing spot rates using a process called bootstrapping.
This article explains how to derive spot rates from par bonds, ensuring a no-arbitrage framework.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 06. octobre 2024
To price an interest rate swap (IRS), you find the fixed rate (C) that makes the present value of the fixed leg's cash flows equal to the floating leg's present value. The fixed leg's value is the sum of discounted fixed payments, while the floating leg approximates the notional principal.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 30. septembre 2024
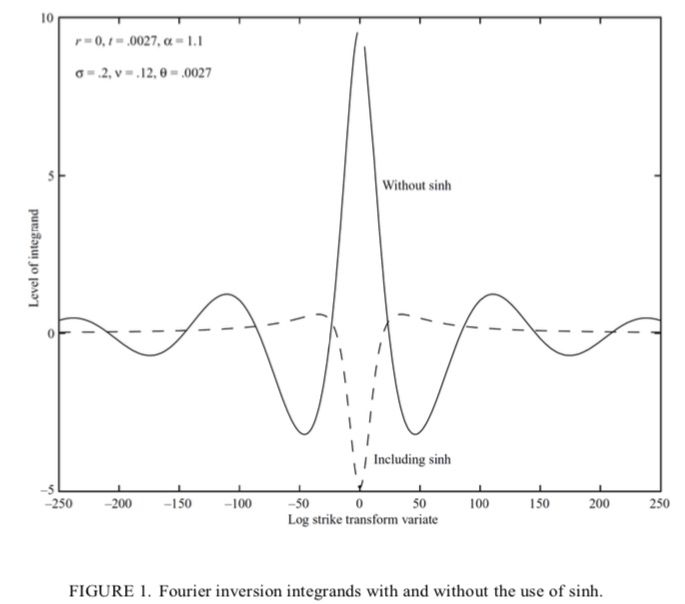
Option pricing, a key financial market challenge, relies on the Fourier transform to address complexities in valuation. An option grants the right to buy or sell an asset at a strike price, K, by expiration, T. The current price depends on the expected payoff, e.g., for a European call: max(S_T - K, 0). This is challenging as future asset prices follow complex stochastic processes.
The Fourier transform simplifies this by converting payoff calculations from time to frequency domain.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 23. septembre 2024
A swaption is an option to enter a future interest rate swap, with two types: a payer swaption (benefits from rising rates) and a receiver swaption (benefits from falling rates). Used for hedging or speculation, swaptions are valued using the forward swap rate, the zero-coupon curve, and implied volatility. Black’s model is often applied for pricing by considering factors like notional, strike rate, and volatility.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 11. novembre 2023
The Jump-to-Default Approach in option trading, modeled by an SDE, highlights how sudden stock price drops (J) affect low strike call options, especially under high credit risk. This contrasts with the Black-Scholes model, which assumes continuous price movements. In high-risk scenarios, the market often lowers the value of these options, factoring in potential defaults, and adjusts implied volatility accordingly. #OptionPricing #CreditRisk #FinancialMarkets #TradingStrategies #InvestmentRisk
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 04. novembre 2023
Mean square hedging minimizes the gap between a hedging portfolio and an exotic option's payoff at maturity. It involves dynamic adjustments of holdings in risky and risk-free assets, guided by solving a stochastic differential equation and often requiring numerical methods like Monte Carlo simulations for implementation.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 03. novembre 2023
Le modèle de Cheyette est un outil financier complexe pour prédire les mouvements des taux d'intérêt, prenant en compte la réversion à la moyenne et la volatilité variables dans le temps. Il est plus sophistiqué que des modèles plus simples comme celui de Vasicek en raison de ses paramètres détaillés, ce qui le rend robuste mais également plus intensif en calculs et moins couramment utilisé en pratique.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 03. octobre 2023
Stopping time helps optimize the exercise of exotic options to maximize payoff. It aids in deciding when to exercise these complex, event-conditioned options before expiry. Specialized models beyond Black-Scholes, like Binomial Tree, address this by balancing immediate vs. future exercise values. #StoppingTime #ExoticOptions
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 10. juin 2023
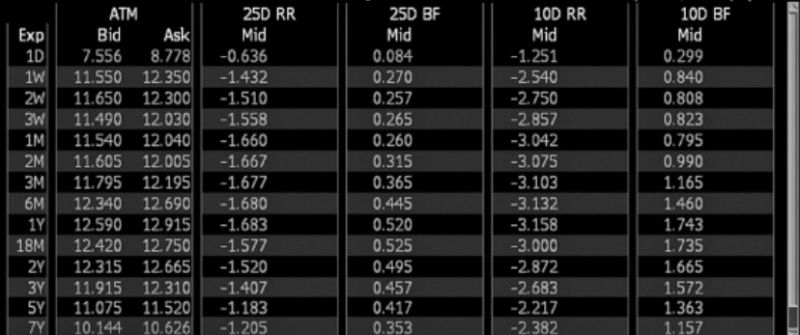
In the world of foreign exchange (FX), two indicators help traders decode market mood: Risk Reversal (RR) and Butterfly (BF) volatilities. Imagine RR as a compass, pointing to bullish or bearish winds by comparing the price expectations of currency going up (call options) to it going down (put options). On the other hand, BF is like a barometer, forecasting calm or stormy weather by measuring the expected price stability of currencies.