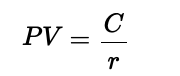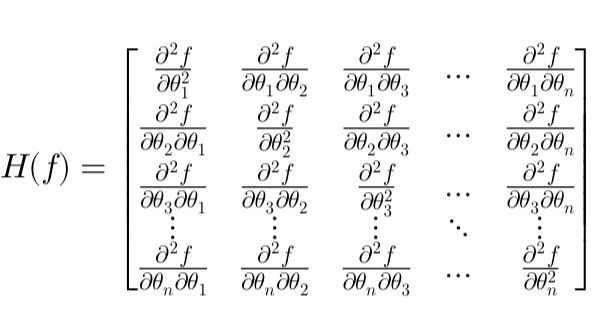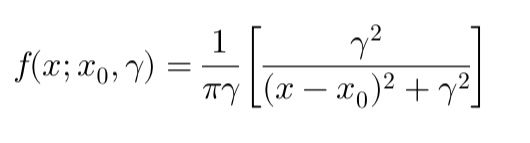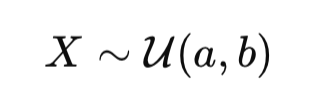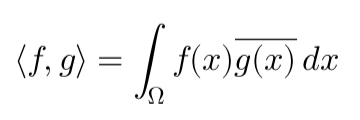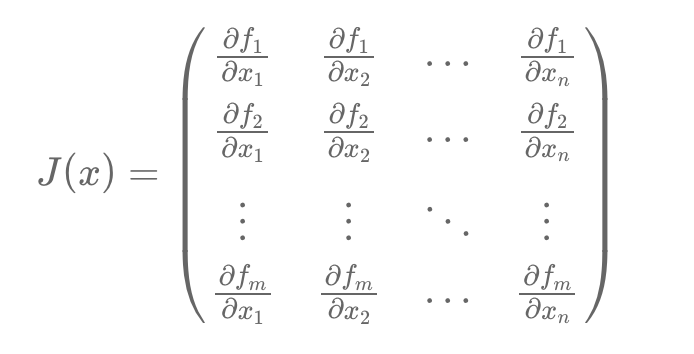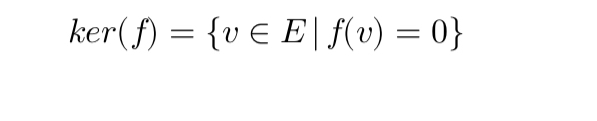Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 13. mars 2025
A perpetuity is a financial instrument that provides endless cash flows. It is used in valuing stocks with fixed dividends, real estate with stable income, perpetual bonds, and corporate valuation. When payments grow over time, the value increases, making it useful for estimating rising future cash flows. Based on geometric series, perpetuities are essential in finance for discounting long-term income streams.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 05. mars 2025
The Hessian matrix, composed of second-order partial derivatives, is a fundamental tool in financial optimization and derivatives pricing. This article simplifies the Hessian’s role in identifying critical points, quadratic approximations, and risk management through Gamma hedging.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 01. mars 2025
This article explains Gradient Descent in simple terms, covering its mathematical foundation and applications in finance, particularly in calibrating the Hull-White model for interest rate modeling. It breaks down the gradient, its role in optimization, and how it minimizes errors iteratively. Key steps in calibrating volatility (σ) using gradient descent are outlined with a practical example.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 28. février 2025
The Cauchy distribution challenges traditional financial models due to its infinite variance and heavy tails. Unlike the mean, which does not exist, the median is a more reliable measure for analyzing returns. This impacts portfolio diversification and risk models, making metrics like standard deviation ineffective. To better manage uncertainty, use the Interquartile Range (IQR) and Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR) for more robust risk assessment.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 25. février 2025
The uniform law is a fundamental concept in quantitative finance, widely used in Monte Carlo simulations, stochastic differential equations (SDEs), and copula models for risk assessment. This article explains how the cumulative distribution function (CDF) and its inverse transform probabilities into standardized shocks, essential for modeling asset price movements.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 10. janvier 2025
Learn how PCA and SVD simplify financial data by identifying key factors. Discover their role in analyzing relationships between factors (e.g., interest rates) and assets, reducing complexity, and enhancing portfolio management and risk assessment.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 25. décembre 2024
Explore the differences between Euclidean spaces, pre-Hilbert spaces, and Hilbert spaces in quantitative finance. Understand their roles in portfolio optimization, Monte Carlo simulations, and stochastic modeling. Learn how these mathematical frameworks handle finite and infinite dimensions, ensuring accuracy in risk measurement and option pricing. Ideal for quants and financial analysts seeking deeper theoretical and computational insights.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 25. décembre 2024
Discover how the Jacobian Matrix plays a crucial role in quantitative finance, from pricing bonds and risk management to sensitivity analysis and yield curve modeling. This article breaks down the mathematical principles behind the Jacobian Matrix and demonstrates its practical applications in analyzing interest rate movements, par rates, and zero rates.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 21. décembre 2024
The Cauchy problem solves differential equations with specific initial conditions, widely applied in modeling dynamic systems in physics, engineering, and finance. It addresses both ordinary differential equations (ODEs) for deterministic systems and stochastic differential equations (SDEs) for random processes, such as asset price modeling.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 20. décembre 2024
The kernel, a key concept in linear algebra, identifies vectors mapped to zero by a linear transformation. Representing a subspace, it reveals inefficiencies and redundancies in financial models. For example, the kernel of a covariance matrix in portfolio management highlights linear combinations of redundant assets, guiding optimization by removing overlaps.