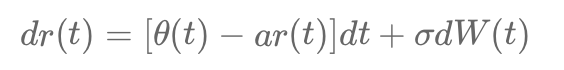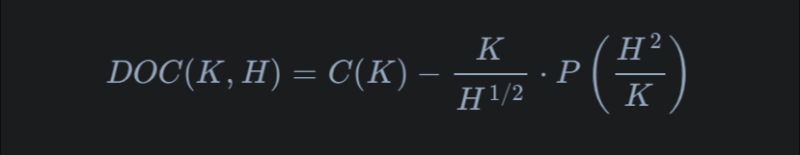Risk Management · 19. février 2025
Le wrong-way risk survient lorsqu'une contrepartie a une probabilité de défaut qui augmente précisément au moment où l'exposition d'une banque à cette contrepartie augmente également, amplifiant ainsi le risque financier. Ce phénomène est particulièrement pertinent dans les transactions sur dérivés et de financement, où les fluctuations du marché influencent l'exposition.
Risk Management · 16. février 2025
Wrong-way risk arises when a counterparty’s likelihood of default increases precisely when a bank’s exposure to it is also rising, amplifying financial risk. This is particularly relevant in derivatives and financing transactions where market fluctuations drive exposure.
Unlike traditional credit risk, which is one-sided, counterparty credit risk in derivatives is bilateral and dynamic, changing with market conditions.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 19. avril 2024
Understanding the probability of events like bond defaults requires recognizing that individual likelihoods, or marginal distributions, don't inherently reveal the likelihood of multiple bonds defaulting simultaneously. Even if two sets of bonds have identical marginal probabilities, their joint probabilities can differ significantly based on default correlations.
Marginal distributions describe individual behavior without considering other variables.
Stochastic Models and Processes · 12. novembre 2023
The Hull-White model is a versatile framework for modeling short-term interest rates and credit risk. It captures the stochastic behavior of rates or hazard rates, ensuring flexibility and accuracy in pricing derivatives like bonds and Credit Default Swaps (CDS). By modeling hazard rates, the model calculates survival and default probabilities, enabling dynamic risk assessment.
15. juillet 2023
In simple terms, think of hedging like insurance. A bank sold a specific type of "insurance" (Down-and-Out European Call) that pays out only if the stock price doesn't dip below a certain level (the barrier). To safeguard itself, the bank uses a mix of buying and selling other financial "insurances" (call and put options). The magic formula ensures that if the stock dips below the barrier, the bank won't lose money. It's a balancing act, where buying one thing counteracts the selling of another