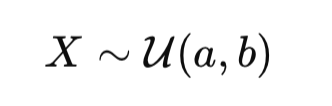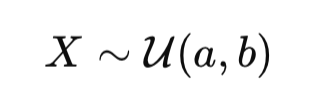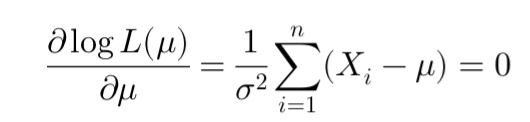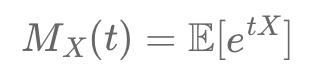Principes mathématiques et applications en finance · 25. février 2025
La loi uniforme est un concept fondamental en finance quantitative, largement utilisée dans les simulations de Monte-Carlo, les équations différentielles stochastiques (EDS) et les modèles de copules pour l’évaluation des risques. Cet article explique comment la fonction de répartition (CDF) et son inverse transforment les probabilités en chocs standardisés, essentiels pour modéliser les mouvements des prix des actifs.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 25. février 2025
The uniform law is a fundamental concept in quantitative finance, widely used in Monte Carlo simulations, stochastic differential equations (SDEs), and copula models for risk assessment. This article explains how the cumulative distribution function (CDF) and its inverse transform probabilities into standardized shocks, essential for modeling asset price movements.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 12. octobre 2024
Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) is a statistical method used to estimate the parameters of a model based on observed data. It identifies the parameter values that maximize the likelihood of the observed data. MLE is widely used in finance, such as in estimating risk metrics like Value-at-Risk and Expected Shortfall by fitting models like the Generalized Pareto Distribution to extreme events.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 19. avril 2024
Understanding the probability of events like bond defaults requires recognizing that individual likelihoods, or marginal distributions, don't inherently reveal the likelihood of multiple bonds defaulting simultaneously. Even if two sets of bonds have identical marginal probabilities, their joint probabilities can differ significantly based on default correlations.
Marginal distributions describe individual behavior without considering other variables.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 13. novembre 2023
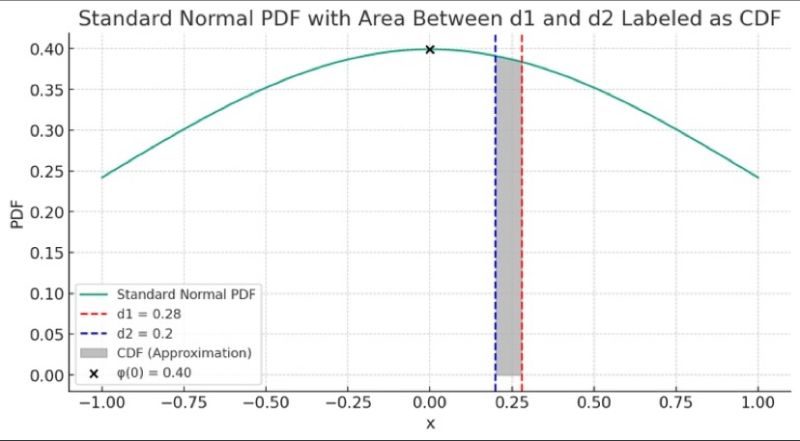
The article explains the connection between the Probability Density Function (PDF) and the Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) in the context of the standard normal distribution. It highlights how the PDF measures the likelihood of a variable at a specific point, while the CDF calculates the probability of the variable being less than or equal to a given value.
Statistics · 01. juillet 2023
Discover the **Moment Generating Function (MGF)**, a tool to analyze random variable distributions. Learn how \( M_X(t) = \mathbb{E}[e^{tX}] \) reveals moments like mean and variance, supporting financial modeling, stock analysis, and risk management. Explore its practical uses in finance today!