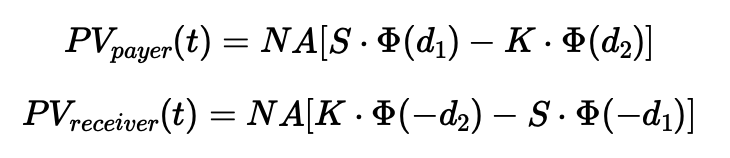Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 30. septembre 2024
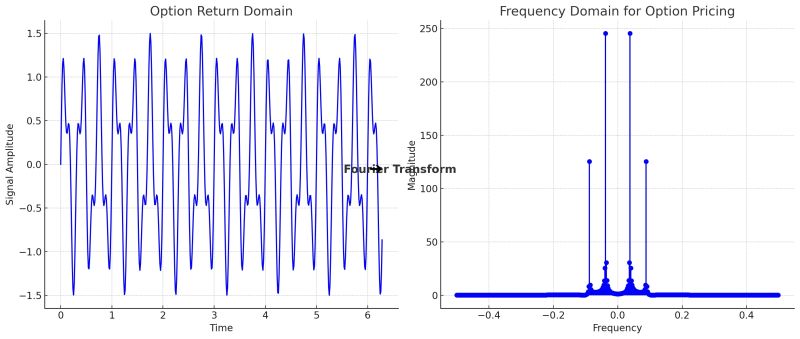
Option pricing, a key financial market challenge, relies on the Fourier transform to address complexities in valuation. An option grants the right to buy or sell an asset at a strike price, K, by expiration, T. The current price depends on the expected payoff, e.g., for a European call: max(S_T - K, 0). This is challenging as future asset prices follow complex stochastic processes.
The Fourier transform simplifies this by converting payoff calculations from time to frequency domain.
Pricing et Valorisation d'instruments financiers · 23. septembre 2024
Une swaption est une option permettant d’entrer dans un swap de taux d'intérêt futur, avec deux types : une payer swaption (bénéficiant de la hausse des taux) et une receiver swaption (bénéficiant de la baisse des taux). Utilisées pour la couverture ou la spéculation, les swaptions sont évaluées à l'aide du taux de swap à terme, de la courbe zéro-coupon et de la volatilité implicite.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 23. septembre 2024
A swaption is an option to enter a future interest rate swap, with two types: a payer swaption (benefits from rising rates) and a receiver swaption (benefits from falling rates). Used for hedging or speculation, swaptions are valued using the forward swap rate, the zero-coupon curve, and implied volatility. Black’s model is often applied for pricing by considering factors like notional, strike rate, and volatility.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 10. juin 2024
Le modèle de Black-Scholes évalue les options européennes en supposant une distribution log-normale des prix d’actions. La formule :
C = S₀ * N(d₁) - X * e^{-rT} * N(d₂)
avec \( d₁ \) et \( d₂ \) standardisant les variables pour le prix de l'action, l'exercice, la volatilité et le temps. Le terme σ²/2 ajuste la distribution log-normale, et σ√T standardise les calculs, facilitant l'estimation de la valeur de l'option.
10. juin 2024
Le temps d'arrêt est clé dans la tarification des options exotiques, permettant d'optimiser le moment d'exercice pour maximiser le rendement. Contrairement aux options standards, leur complexité nécessite des modèles spécifiques tels que les arbres binomiaux ou Monte Carlo. La valeur est déterminée en comparant la valeur de conservation de l'option et la valeur d'exercice immédiat.