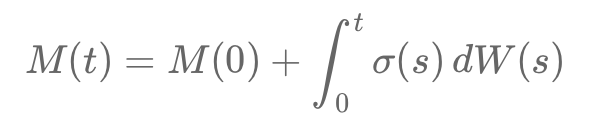Stochastic Models and Processes · 05. octobre 2023
Explore the roots of the martingale concept, originally a betting strategy in fair games, and its evolution in quantitative finance. Uncover the role of unpredictability and risk, dispelling "sure-win" myths. #Finance #Martingale #RiskManagement
Stochastic Models and Processes · 04. octobre 2023
Brownian motion bridges Martingale's unpredictability and Markov's memorylessness, essential in quantitative finance for pricing derivatives and risk management. It illustrates a random yet memoryless movement, pivotal in financial mathematical modeling. #Finance #QuantitativeFinance
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 03. octobre 2023
Stopping time helps optimize the exercise of exotic options to maximize payoff. It aids in deciding when to exercise these complex, event-conditioned options before expiry. Specialized models beyond Black-Scholes, like Binomial Tree, address this by balancing immediate vs. future exercise values. #StoppingTime #ExoticOptions
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 03. octobre 2023
Ocone martingales offer stable modeling for complex, dynamic financial systems due to their unique invariance, aiding in exotic option pricing. Rooted in control theory, they ensure consistent statistical properties under specific mathematical manipulations. #FinancialMath #Martingales
26. août 2023
In finance and mathematical finance, a numéraire is a chosen unit of account or reference measure that allows for the pricing and valuation of financial instruments. It is used to express the relative value of different assets and cash flows. The concept of a numéraire is particularly useful in risk-neutral pricing and the evaluation of derivative securities. Here's how a numéraire works: 1. Choice of Numéraire: choose a specific financial instrument or asset to serve as the numéraire: a...
05. août 2023
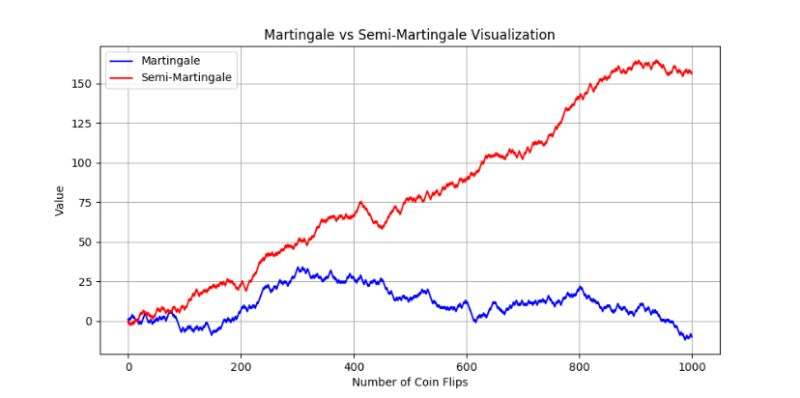
Delve into the world of probability with martingales and semi-martingales. The former mirrors a fair coin flip game, while the latter adds a steady gain, blending unpredictability with trends. Essential in finance for modeling asset prices, these concepts juxtapose randomness with predictability. Visualized through 1,000 coin flips, it's a journey from simple games to profound math insights. #Martingale #SemiMartingale #CoinFlip #ProbabilityTheory.