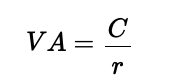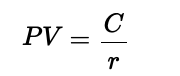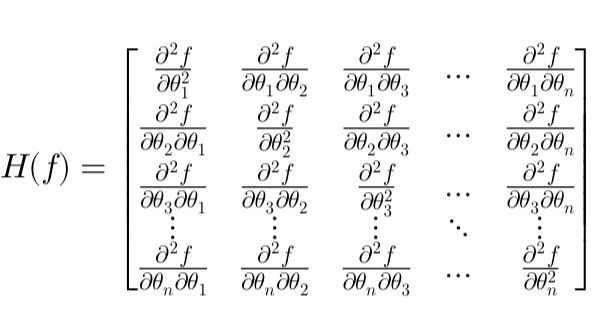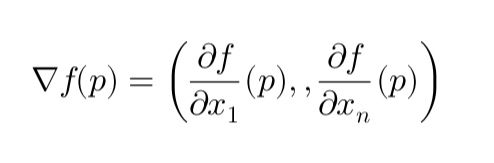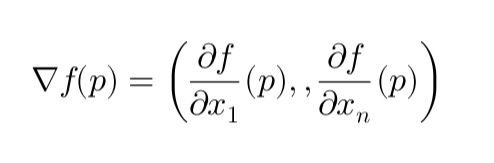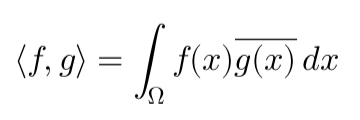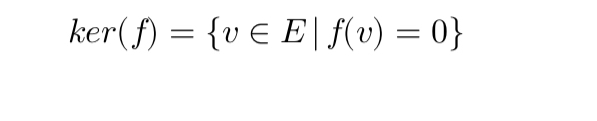Principes mathématiques et applications en finance · 13. mars 2025
Une perpétuité est un instrument financier qui fournit des flux de trésorerie sans fin. Elle est utilisée pour évaluer des actions avec des dividendes fixes, l’immobilier avec des revenus stables, les obligations perpétuelles et la valorisation des entreprises. Lorsque les paiements augmentent au fil du temps, la valeur s’accroît, ce qui en fait un outil utile pour estimer des flux de trésorerie futurs en hausse.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 13. mars 2025
A perpetuity is a financial instrument that provides endless cash flows. It is used in valuing stocks with fixed dividends, real estate with stable income, perpetual bonds, and corporate valuation. When payments grow over time, the value increases, making it useful for estimating rising future cash flows. Based on geometric series, perpetuities are essential in finance for discounting long-term income streams.
Processus et Modèles Stochastiques · 05. mars 2025
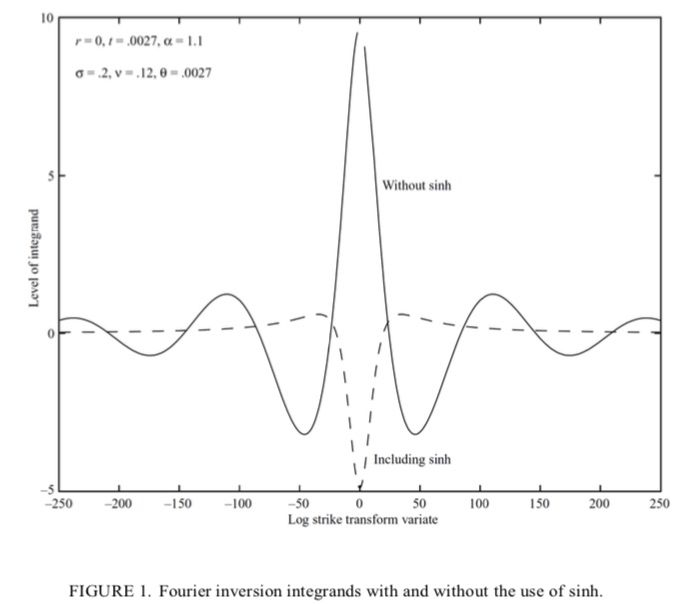
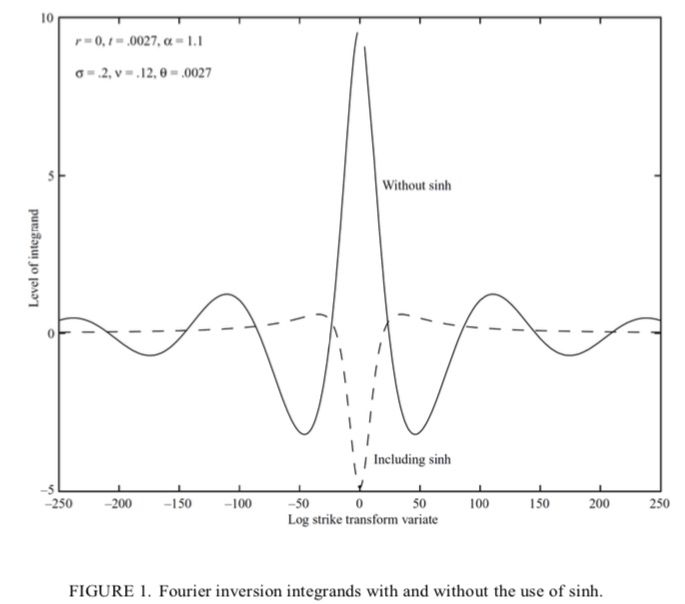
Découvrez comment la méthode de Carr & Madan exploite la transformée de Fourier pour la valorisation des options. Explorez les concepts clés, apprenez à atténuer les instabilités et améliorez les calculs numériques.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 05. mars 2025
Learn how the Carr & Madan method leverages the Fourier Transform for option pricing. Discover key concepts, how to mitigate instabilities, and improve numerical computations.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 05. mars 2025
The Hessian matrix, composed of second-order partial derivatives, is a fundamental tool in financial optimization and derivatives pricing. This article simplifies the Hessian’s role in identifying critical points, quadratic approximations, and risk management through Gamma hedging.
Principes mathématiques et applications en finance · 01. mars 2025
Cet article explique la descente de gradient en termes simples, en couvrant ses bases mathématiques et ses applications en finance, notamment dans la calibration du modèle de Hull-White pour la modélisation des taux d’intérêt. Il détaille le gradient, son rôle dans l’optimisation et la manière dont il minimise les erreurs de façon itérative. Les étapes clés de la calibration de la volatilité (σ) par descente de gradient sont présentées avec un exemple pratique.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 01. mars 2025
This article explains Gradient Descent in simple terms, covering its mathematical foundation and applications in finance, particularly in calibrating the Hull-White model for interest rate modeling. It breaks down the gradient, its role in optimization, and how it minimizes errors iteratively. Key steps in calibrating volatility (σ) using gradient descent are outlined with a practical example.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 10. janvier 2025
Learn how PCA and SVD simplify financial data by identifying key factors. Discover their role in analyzing relationships between factors (e.g., interest rates) and assets, reducing complexity, and enhancing portfolio management and risk assessment.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 25. décembre 2024
Explore the differences between Euclidean spaces, pre-Hilbert spaces, and Hilbert spaces in quantitative finance. Understand their roles in portfolio optimization, Monte Carlo simulations, and stochastic modeling. Learn how these mathematical frameworks handle finite and infinite dimensions, ensuring accuracy in risk measurement and option pricing. Ideal for quants and financial analysts seeking deeper theoretical and computational insights.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 20. décembre 2024
The kernel, a key concept in linear algebra, identifies vectors mapped to zero by a linear transformation. Representing a subspace, it reveals inefficiencies and redundancies in financial models. For example, the kernel of a covariance matrix in portfolio management highlights linear combinations of redundant assets, guiding optimization by removing overlaps.