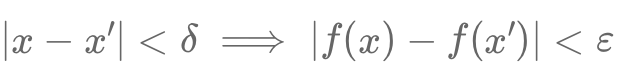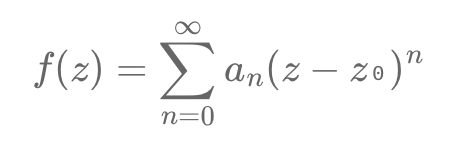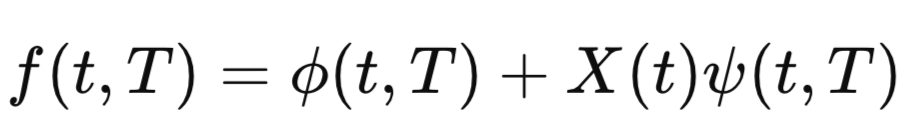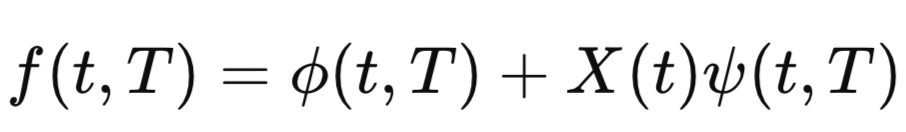Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 01. octobre 2024
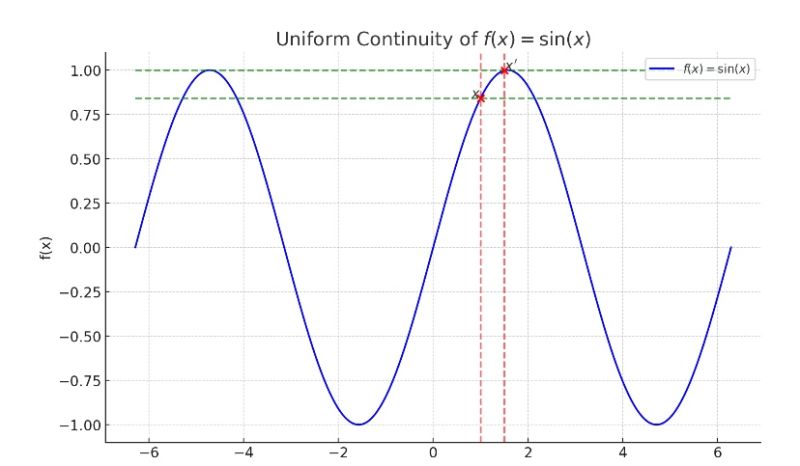
En mathématiques, la continuité est un concept fondamental qui nous aide à comprendre le comportement des fonctions. Si la notion standard de continuité est généralement suffisante pour les applications de base, il existe une version plus forte, appelée continuité uniforme. Heinrich Heine a introduit le concept de continuité uniforme en 1872 lorsqu’il a publié une démonstration du théorème aujourd’hui connu sous le nom de théorème de Heine pour les fonctions continues sur un...
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 01. octobre 2024
Uniform continuity is a key concept in mathematical analysis that extends the standard idea of continuity by ensuring consistent behavior of functions across entire intervals. Introduced by Heinrich Heine in 1872 and rooted in earlier work by Dirichlet (1854), it plays a critical role in advanced mathematics and real-world applications.
Pointwise Continuity: Focuses on local behavior at individual points.
Uniform Continuity: Ensures predictability across an entire domain using
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 01. octobre 2024
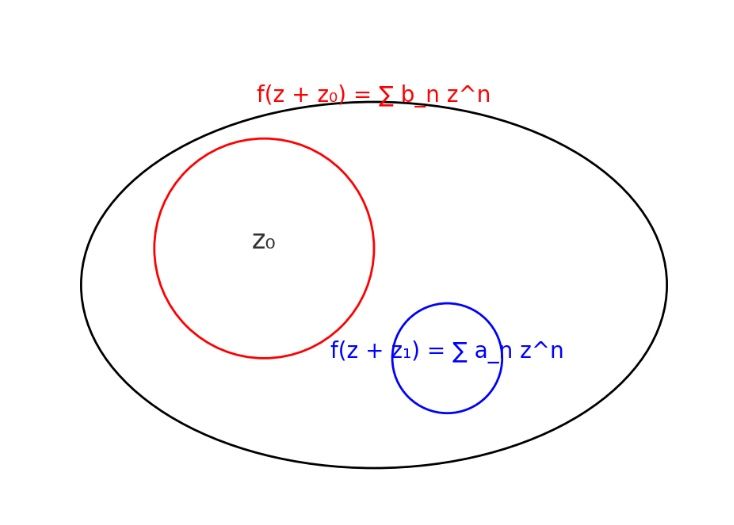
In quantitative finance, pricing conditional derivatives, like options, requires ensuring that price functions converge, meaning they stabilize as calculations are refined. Compact and closed sets in complex space help ensure this stability by keeping sequences bounded and finite. Analytic functions, which smoothly represent derivative prices, rely on this convergence for accuracy.
The Cauchy integral formula enables finding a function's value by integrating along a boundary contour.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 01. octobre 2024
En finance quantitative, la valorisation des dérivés conditionnels, tels que les options, nécessite la convergence des fonctions de prix. Les ensembles compacts et fermés dans l’espace complexe assurent cette stabilité. Les fonctions analytiques dépendent de cette convergence pour une précision optimale, et la formule intégrale de Cauchy permet de calculer la valeur d'une fonction via une intégrale sur son contour.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 03. novembre 2023
Le modèle de Cheyette est un outil financier complexe pour prédire les mouvements des taux d'intérêt, prenant en compte la réversion à la moyenne et la volatilité variables dans le temps. Il est plus sophistiqué que des modèles plus simples comme celui de Vasicek en raison de ses paramètres détaillés, ce qui le rend robuste mais également plus intensif en calculs et moins couramment utilisé en pratique.
Stochastic Models and Processes · 03. novembre 2023
The Cheyette Model is a complex financial tool for predicting interest rate movements, accounting for time-varying mean reversion and volatility. It's more intricate than simpler models like Vasicek due to its detailed parameters, which makes it robust but computationally intensive and less commonly used in practice.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 01. novembre 2023
The Crank-Nicolson Method, pivotal in quantitative finance, adeptly solves PDEs for option pricing and interest rate modeling. It splits time and space into grids, balancing calculations between current and next steps (implicit and explicit). It's stable and precise, essential for real-world financial scenarios.