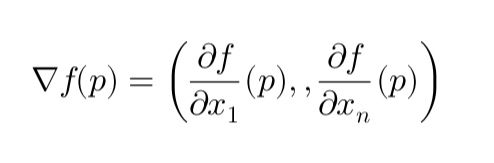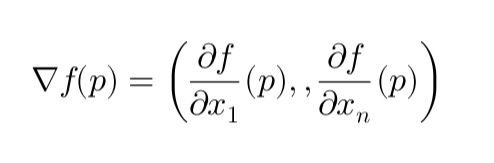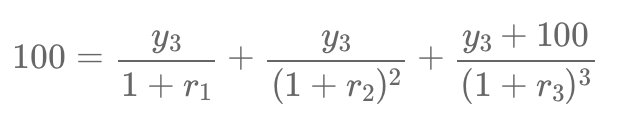Principes mathématiques et applications en finance · 01. mars 2025
Cet article explique la descente de gradient en termes simples, en couvrant ses bases mathématiques et ses applications en finance, notamment dans la calibration du modèle de Hull-White pour la modélisation des taux d’intérêt. Il détaille le gradient, son rôle dans l’optimisation et la manière dont il minimise les erreurs de façon itérative. Les étapes clés de la calibration de la volatilité (σ) par descente de gradient sont présentées avec un exemple pratique.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 01. mars 2025
This article explains Gradient Descent in simple terms, covering its mathematical foundation and applications in finance, particularly in calibrating the Hull-White model for interest rate modeling. It breaks down the gradient, its role in optimization, and how it minimizes errors iteratively. Key steps in calibrating volatility (σ) using gradient descent are outlined with a practical example.
Pricing and Valuing Financial Instruments · 02. février 2025
In fixed-income markets, spot rates are crucial for pricing bonds and detecting arbitrage opportunities. However, financial markets typically provide par rates instead of spot rates, making it essential to extract missing spot rates using a process called bootstrapping.
This article explains how to derive spot rates from par bonds, ensuring a no-arbitrage framework.
Mathematical Principles and Quantitative Finance · 13. novembre 2023
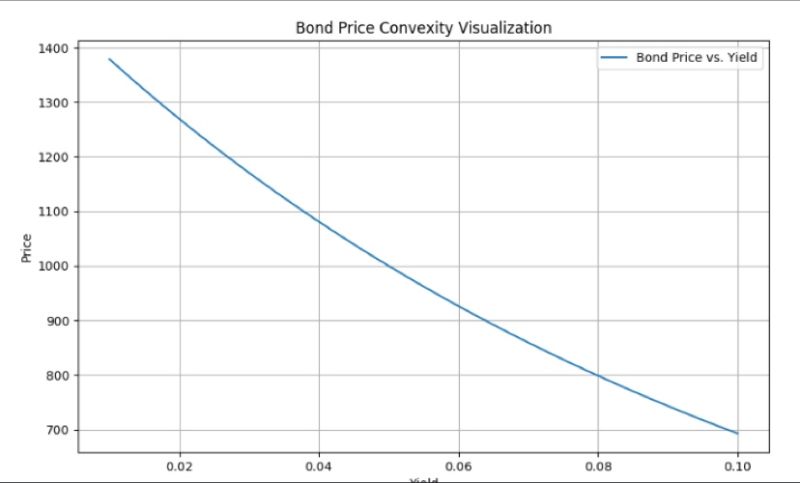
Bond convexity describes the curve-like relationship between bond prices and interest rates, causing prices to rise more when rates drop than they fall when rates rise. This curvature means bond price changes are not linear and convexity corrects pricing models, especially for large rate moves. #BondConvexity